Graphs
A graph is a non-linear data structure that can be looked at as a collection of vertices (or nodes) potentially connected by line segments named edges.
Here is some common terminology used when working with Graphs:
1- Vertex - A vertex, also called a “node”, is a data object that can have zero or more adjacent vertices. 2- Edge - An edge is a connection between two nodes. 3- Neighbor - The neighbors of a node are its adjacent nodes, i.e., are connected via an edge. 4- Degree - The degree of a vertex is the number of edges connected to that vertex.
Challenge 35
Features
Implement your own Graph. The graph should be represented as an adjacency list, and should include the following methods:
add node
- Arguments: value
- Returns: The added node
- Add a node to the graph
add edge
- Arguments: 2 nodes to be connected by the edge, weight (optional)
- Returns: nothing
- Adds a new edge between two nodes in the graph
If specified, assign a weight to the edge. Both nodes should already be in the Graph
get nodes
- Arguments: none
- Returns all of the nodes in the graph as a collection (set, list, or similar)
get neighbors
- Arguments: node
- Returns a collection of edges connected to the given node
Include the weight of the connection in the returned collection
size
- Arguments: none
- Returns the total number of nodes in the graph
Challenge 36
Write the following method for the Graph class:
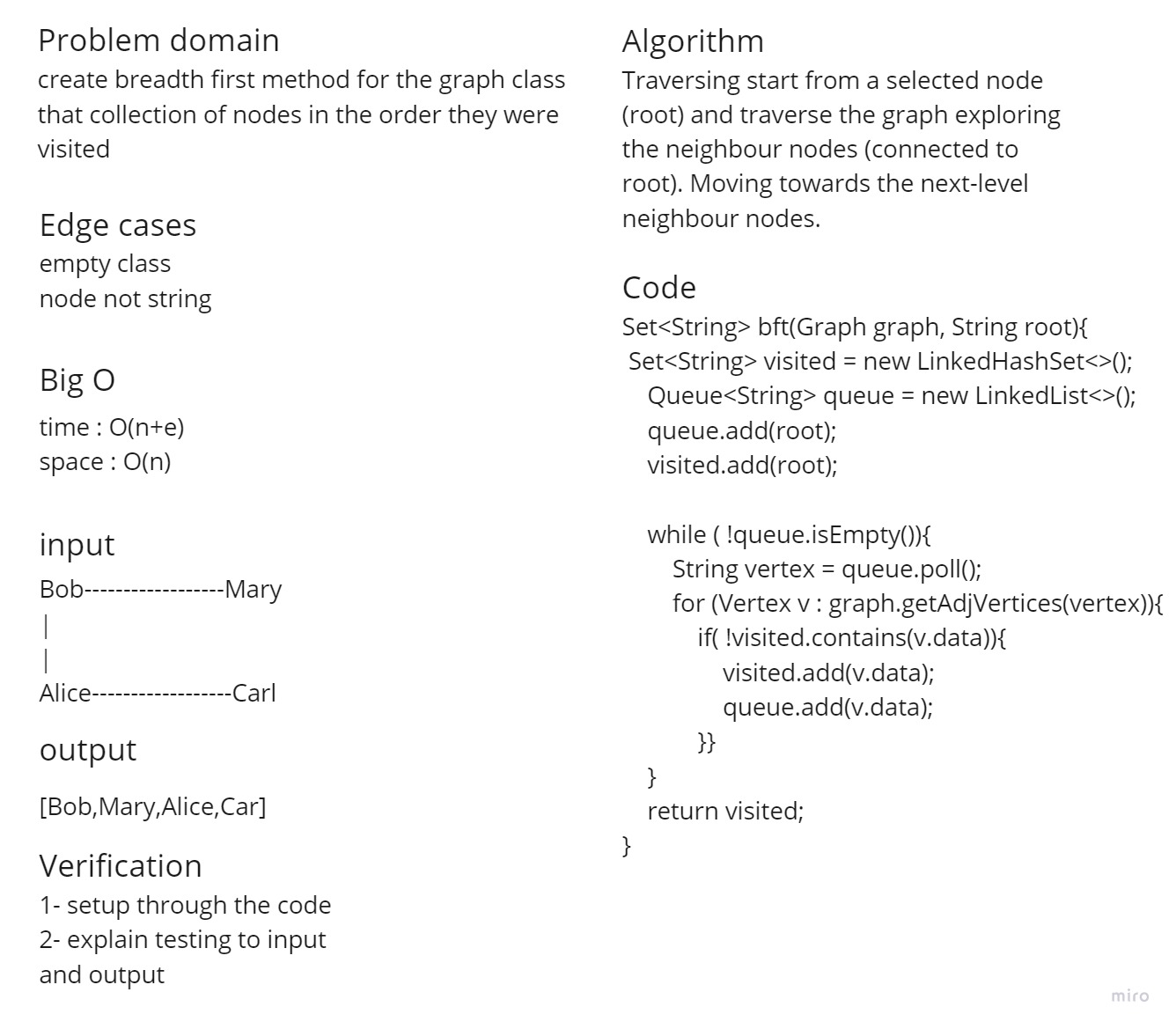
- breadth first
- Arguments: Node
- Return: A collection of nodes in the order they were visited.
- Display the collection
Whiteboard Process
Approach & Efficiency
Traversing starts from a selected node (root) and traverse the graph exploring the neighbour nodes (connected to root). Moving towards the next-level neighbour nodes.
Big (O)
Time Complexity : O(n+e) space Complexity : O(n)
Challenge 37
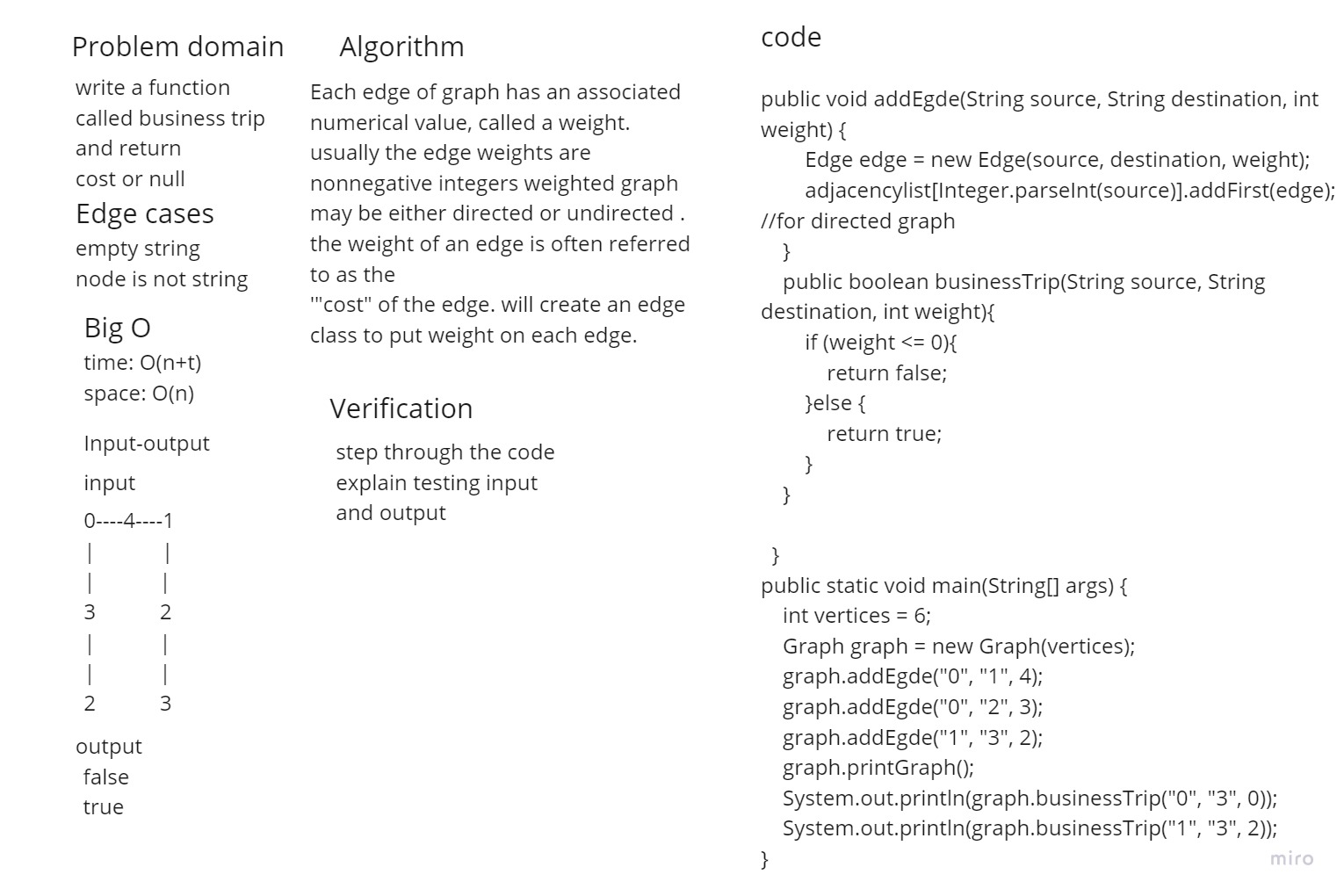
Write a function called business trip:
- Arguments: graph, array of city names
- Return: cost or null
- Determine whether the trip is possible with direct flights, and how much it would cost.
Whiteboard Process
Approach & Efficiency
A Graph is called weighted graph when it has weighted edges which means there are some cost associated with each edge in graph.
Implementation:
Each edge of a graph has an associated numerical value, called a weight. Usually, the edge weights are nonnegative integers. Weighted graphs may be either directed or undirected. The weight of an edge is often referred to as the “cost” of the edge. Will create an Edge class to put weight on each edge
Big (O)
Time Complexity : O(n+e) space Complexity : O(n)
Challenge 38
Write the following method for the Graph class:
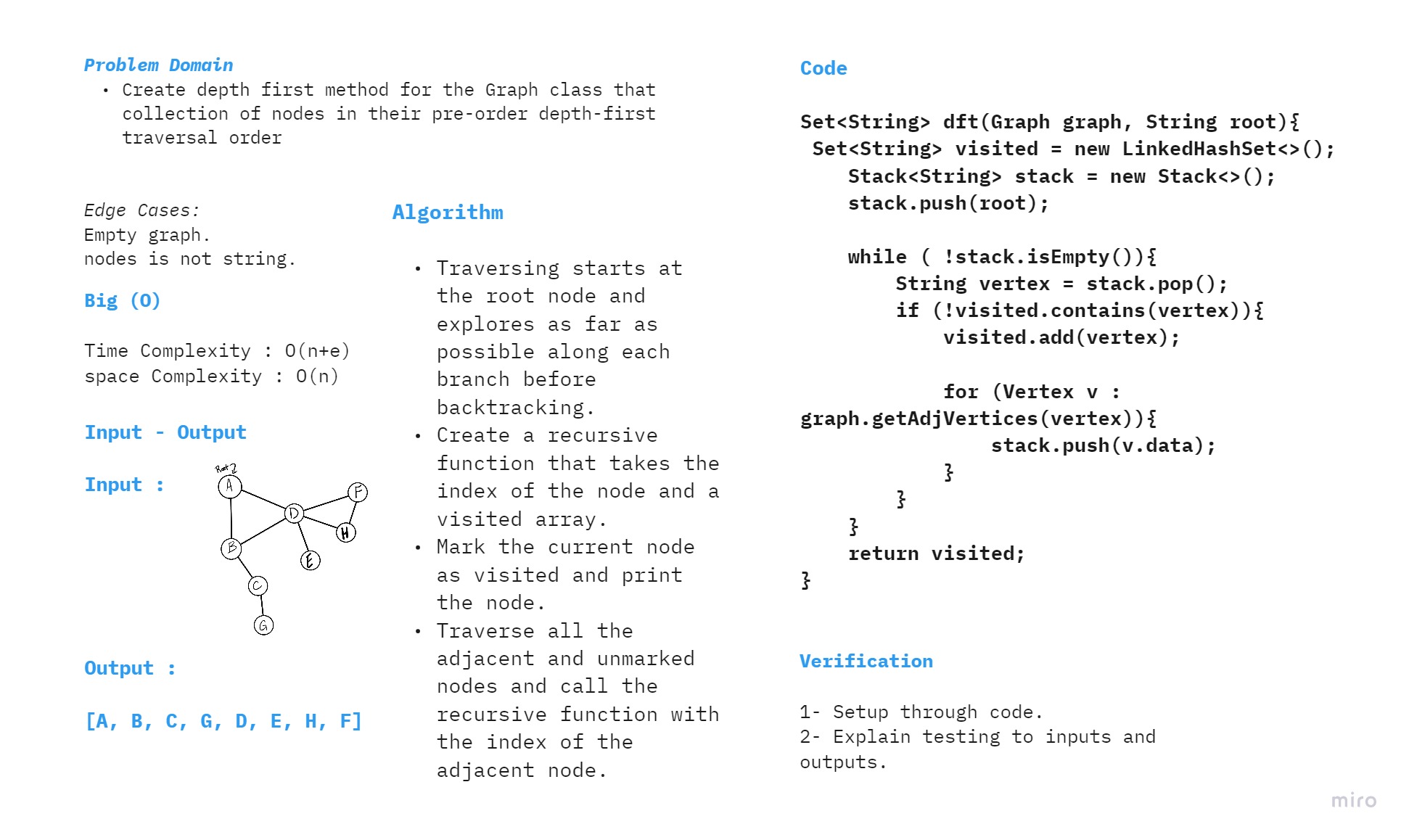
depth first
- Arguments: Node (Starting point of search)
- Return: A collection of nodes in their pre-order depth-first traversal order
- Display the collection
Whiteboard Process
Approach & Efficiency
- Traversing starts at the root node and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
- Create a recursive function that takes the index of the node and a visited array.
- Mark the current node as visited and print the node.
-
Traverse all the adjacent and unmarked nodes and call the recursive function with the index of the adjacent node.
- Big (O)
Time Complexity : O(n+e) space Complexity : O(n)